What is Blockchain? Why use Blockchain?
- Blockchain
Blockchain is the latest technology that works on the principle of record-keeping. This technology also ensures that data cannot be forged, or systems cannot be hacked enabling security for data, systems, and data immutability (cannot create a copy) in any business network. This means that the data once entered cannot be changed or manipulated and is very difficult to change or hack.
It works on distributed ledger technology (DLT), which helps digital systems to record transactions, track assets and data from multiple places at the same time. In other words it is also known as digital ledger or digital asset.
An asset can be tangible or intangible. Tangible like vehicles (cars, vans), property (land, house), monetary asset. Intangible can be patents, branding, Intellectual property copyrights, shares, financial instruments of product or any organization and cryptocurrency (Bitcoin) etc. So, in simple words anything which has value can be tracked and traded virtually using Blockchain Techniques, in-return the risk reduces and costs are cut.
In Blockchain, every transaction in a ledger is authorised by digital signature of the respective owner, which authenticates the transaction and safeguards the data where encrypted blocks of digital asset data is stored and chained so that it is free from getting tampered or copied. So, the data in the digital ledger is supposed to be in highly secure environment.
The digital ledgers or digital assets can only be distributed but cannot be copied or transferred to anybody. These ledgers or assets are decentralized allowing transparency which means all the changes made are documented, with real time accessibility and governance among at least two or more parties.
To understand in simple words, digital ledger is similar to Google spreadsheets which are shared among multiple users using different computer systems in the network. The google sheet data can be viewed by anybody using that network and all the users with whom the document is shared are looking at the same document at the same time and there is no copy that is getting created here and data cannot get corrupted by anyone as well. In other words, this creates a decentralized distribution chain environment where everyone can look at the base document at the same time and all the modifications are visible to everyone so there is transparency in the data among all the users in the real time scenarios. However, the original content in the document cannot be edited by any user unlike the way it can be edited in Google documents. Adding the information is possible but editing the old document is not possible.
We shall now get to understand how blockchain works in real time. The name blockchain itself reveals how it works. The data or the assets or ledger is stored in the form of blocks and these blocks are attached with a number; these numbers are called as nonce which means number used only once. This is a random number that gets generated and then these numbers generate a block header hash, which means allocating the number permanently to any block of data or asset and it cannot be changed or allocated to any other block. In simple words this hash nonce is similar to bank account numbers or telephone numbers which are unique to each user. While the telephone number can still be transferred, the block number cannot be transferred.
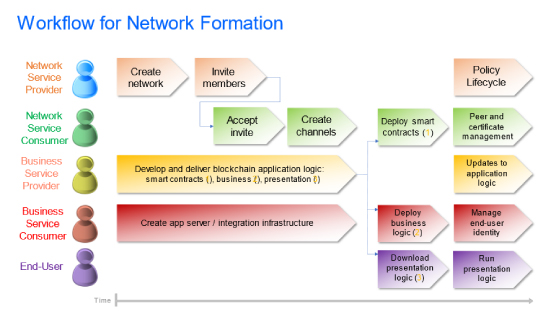
Initially the technology was very confusing for a layman, but it is evolving and becoming more user friendly. Identifying a blockchain use case is not an easy task. However, there are few things that needs to be considered while looking at the use case and they are
- There should be a Business Problem that cannot be solved efficiently by using any technology.
- An Identifiable business network scope, with assets, participants and transactions
- A need for trust
- Consider the pain points such as existing pain points, scope, design points and references
Few Industries in which Blockchain has been used so far:
- Insurance - claim processing,
- Finance -trade finance, mortgages, cross currency payments
- Healthcare- medical records
- Public Sector -citizen identity, asset registration
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Banking
- Supply-chain
- E-commerce
- Sports
- Entertainment
- Real Estate
Types of blockchain:
Public blockchain network: It is open for anybody to join, for e.g. Bitcoin.
Private blockchain network: This is similar to Public Blockchain but decentralized for peer to peer network. It is governed by an organization.
Permission blockchain network: Businesses or Organization that have set up Private Blockchain can also set up permission blockchain. Even the Public Blockchain can set up a permission blockchain network where one can restrict who can join the network.
Consortium blockchain: Multiple organizations can join together to setup Consortium Blockchain network. They can setup which organization will access the data and submit the transactions etc.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency:
Blockchain is well known or famous for Cryptocurrency trading eg. Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum. The very first blockchain was used in 2009 as Bitcoin. This cryptocurrency is similar to digital currency which can be used in trading or buying any goods or services. But cryptocurrency uses blockchain technology, so it is more secure compared to normal digital transactions. There are more than 20,000 cryptocurrencies in the world, Bitcoin is the most popular and holds the highest value. The value of Bitcoin in the market fluctuates in several thousand dollars.

Cryptocurrencies work on blockchain technology making it next to impossible in terms of theft making it more secured currency and transaction. The need for individual currency or any banking system is not required in cryptocurrency trading. Anybody from any part of the world can try to any part of the world without any currency exchange or any central bank involvement.
But there are still arguments or debates in the banking sector whether to consider crypto trading as legal digital currency or not as the trading is very volatile.
FutureSkills Prime: To learn more about the core concepts of blockchain, register on FutureSkills Prime, the technology skilling hub of India and access blockchain courses aligned to industry standards and validated by the Government of India.
Tarakeshwari Junge, 360DigiTMG


